The Best of Both Worlds: A New Take on Metal–Plastic Hybrid 3D Printing
Current 3D printers employ either plastic or metal only, and the conventional method to coat 3D plastic structures with metal is not environment-friendly and yields poor results. Now, scientists from Waseda University, Japan, have developed a metal–plastic hybrid 3D printing technique that produces plastic structures with a highly adhesive metal coating on desired areas. This approach extends the use of 3D printers to 3D electronics for future robotics and Internet-of-Things applications.
Three-dimensional (3D) printing technology has evolved tremendously over the last decade to the point where it is now viable for mass production in industrial settings. Also known as “additive manufacturing,” 3D printing allows one to create arbitrarily complex 3D objects directly from their raw materials. In fused filament fabrication, the most popular 3D printing process, a plastic or metal is melted and extruded through a small nozzle by a printer head and then immediately solidifies and fuses with the rest of the piece. However, because the melting points of plastics and metals are very different, this technology has been limited to creating objects of either metal or plastic only—until now.
In a recent study published in Additive Manufacturing, scientists from Waseda University, Japan, developed a new hybrid technique that can produce 3D objects made of both metal and plastic. Professor Shinjiro Umezu, who led the study, explains their motivation: “Even though 3D printers let us create 3D structures from metal and plastic, most of the objects we see around us are a combination of both, including electronic devices. Thus, we thought we’d be able to expand the applications of conventional 3D printers if we managed to use them to create 3D objects made of both metal and plastic.”
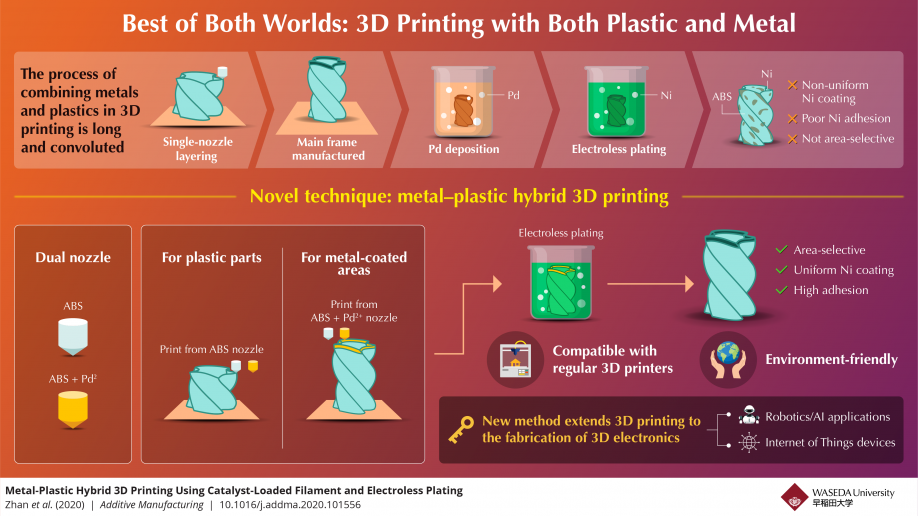
Their method is actually a major improvement over the conventional metallization process used to coat 3D plastic structures with metal. In the conventional approach, the plastic object is 3D-printed and then submerged in a solution containing palladium (Pd), which adheres to the object’s surface. Afterwards, the piece is submerged in an electroless plating bath that, using the deposited Pd as a catalyst, causes dissolved metal ions to stick to the object. While technically sound, the conventional approach produces a metallic coating that is non-uniform and adheres poorly to the plastic structure.
In contrast, in the new hybrid method, a printer with a dual nozzle is used; one nozzle extrudes standard melted plastic (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, or ABS) whereas the other extrudes ABS loaded with PdCl2. By selectively printing layers using one nozzle or the other, specific areas of the 3D object are loaded with Pd. Then, through electroless plating, one finally obtains a plastic structure with a metallic coating over selected areas only.
The scientists found the adhesion of the metal coating to be much higher when using their approach. What’s more, because Pd is loaded in the raw material, their technique does not require any type of roughening or etching of the ABS structure to promote the deposition of the catalyst, unlike the conventional method. This is especially important when considering that these extra steps cause damage not only to the 3D object itself, but to the environment as well, owing to the use of toxic chemicals like chromic acid. Lastly, their approach is entirely compatible with existing fused filament fabrication 3D printers.
Umezu believes that metal–plastic hybrid 3D printing could become very relevant in the near future considering its potential use in 3D electronics, which is the focus of upcoming Internet-of-Things and artificial intelligence applications. In this regard, he adds: “Our hybrid 3D printing method has opened up the possibility of fabricating 3D electronics so that devices and robots used in healthcare and nursing care could become significantly better than what we have today.”
This study hopefully paves the way for hybrid 3D printing technology that will enable us to get the best of both worlds—metal and plastic combined.
***
Reference
Authors: Jing Zhan (a), Takayuki Tamura (b), Gyotong Ri (b), Zhenghao Ma (b), Michinari Sone (c), Masahiro Yoshino (c), Shinjiro Umezu (b), and Hirotaka Sato (a)
Title of original paper: Metal-Plastic Hybrid 3D Printing Using Catalyst-Loaded Filament and Electroless Plating
Journal: Additive Manufacturing
DOI: 10.1016/j.addma.2020.101556
Affiliations:
(a) School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Nanyang Technological University
(b) Department of Modern Mechanical Engineering, Waseda University
(c) Research and Development div., Yoshino Denka Kogyo, Inc.
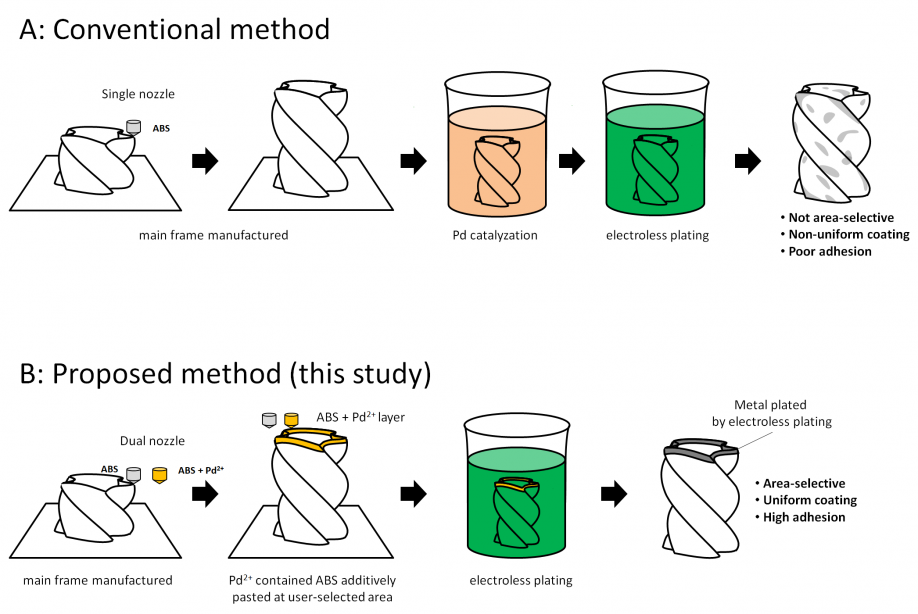
Overview of the conventional and the proposed method for the metallization of a 3D-printed plastic structure. Unlike the conventional technique, the proposed dual-nozzle approach produces 3D objects with a uniform and strongly adhered metallic coating in desired areas only.
About Waseda University
Waseda University is a leading private, non-profit institution of higher education based in central Tokyo, with over 50,000 students in 13 undergraduate and 20 graduate schools. Founded in 1882, Waseda cherishes three guiding principles: academic independence, practical innovation and the education of enlightened citizens. Established to mold future leaders, Waseda continues to fulfill this mission, counting among its alumni seven prime ministers and countless other politicians, business leaders, journalists, diplomats, scholars, scientists, actors, writers, athletes and artists. The University is also number one in Japan in international activities, including the number of international students, with the broadest range of degree programs fully taught in English.
Comments (0)
This post does not have any comments. Be the first to leave a comment below.
Featured Product

