Assessing the health of capital equipment used to produce and move these goods minimizes cost repairs, downtime and outages. Businesses gain a big picture of the logistics chain using wireless sensors that provide data on the location of high-value cargo.
Delivering IoT-Centric Factory Automation with Wi-Fi HaLow Technology
Kevin Daly, Vice President of Sales | Morse Micro
Companies across all industries and geographies are harnessing the power of the Internet of Things (IoT) to derive more value and efficiency from their logistics and supply chains operations. IoT-enabled asset tracking, for example, enables businesses to pinpoint the location and condition of assets, anywhere and anytime throughout the shipping process. According to Data Bridge Market Research, the global market for asset tracking and inventory management solutions will continue to grow steadily in the coming years, reaching $41.24 billion (USD) by 2027 and achieving a market growth rate of 13.7 percent during the 2020-to-2027 forecast period.
End-to-end asset management systems based on IoT platforms provide a comprehensive view of raw materials, works in progress (WIP), finished goods inventory and real-time tracking, extending from the fulfilment process to end-customer delivery. Assessing the health of capital equipment used to produce and move these goods minimizes cost repairs, downtime and outages. Businesses gain a big picture of the logistics chain using wireless sensors that provide data on the location of high-value cargo. Whether a company owns the complete logistics chain or shares resources with other companies, decision makers requires a transparent view of real-time information at every point. Comprehensive supply chain management systems ultimately enable predictable planning, minimal inventory loss, regulatory compliance and satisfied customers.
While corporations recognize the tremendous value that the IoT brings to asset management, the challenge is to seamlessly link remote sensors wirelessly to the internet across multiple sites and indoor/outdoor locations. The ideal wireless technology should be standards-based, cost-effective, low power to sustain long battery life and able to span long distances. Wi-Fi HaLow, an industry-standard wireless solution (IEEE 802.11ah), provides an optimal choice for asset tracking and supply chain systems requiring a secure, bidirectional flow of information. A sub-1 GHz protocol, Wi-Fi HaLow uses narrower channels than 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and the newly added 6 GHz versions of Wi-Fi. Wi-Fi HaLow also provides a low-power, long-range solution at a much higher throughput than any other proprietary wireless technologies that would fall short on reach, data capacity and battery life.
Equipment suppliers can use optimized Wi-Fi HaLow chips and protocol stacks to create wireless asset tags, trackers, scanners and monitors designed to operate across a wide range of distances and data rates. These wireless IoT devices can access the internet through standard HaLow access points (APs) across all logistics and warehousing domains. The following four factory automation and asset management use cases demonstrate the benefits of Wi-Fi HaLow technology for supply chain logistics: tags and trackers, pickers and scanners, large warehouses, factories, and security systems.
Smart Tags and Trackers for Precise Location
Wi-Fi HaLow operates in sub-1 GHz frequencies, using narrower channels than conventional 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi protocols. Wi-Fi HaLow is an ideal wireless technology for tags and trackers because sub-GHz signals reach farther and penetrate objects better than higher frequency protocols at lower total power. HaLow also uses the Wi-Fi standard’s Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) modulation scheme, which enhances the robustness of wireless connections in multipath environments, enabling signals to reflect off of objects.
IoT-connected trackers use long-range wireless networks to enable companies track shipped goods throughout their delivery journeys. Using Wi-Fi HaLow routers, cargo carriers can establish two-way satellite internet connections on trucks, trains, planes, ships and warehouses. Wi-Fi HaLow allows customers to aggregate multiple shipments on board while providing improved connectivity throughout. This capability eliminates concerns about the location of a tag or tracker, even when deployed in numerous containers. Each customer can have separate encrypted L3 tunnels back to their home platforms using internet-ready Wi-Fi HaLow system-on-chip (SoC) devices.
With Wi-Fi HaLow access points on trucks, ships, trains or planes, real-time data from HaLow-enabled sensors can be communicated continuously to all parties along the supply chain. The trackers’ sub-GHz signals can penetrate through bulk materials, enabling connectivity even in densely packed cargo containers. Knowing the precise location and current condition of each container containing perishable goods can help owners determine next steps, such as selecting the best grocery store to receive the shipment at optimal ripeness. Wireless sensor tags can be built using cost-effective coin cell batteries that last for years. The tags can also be reprogrammed and redeployed for future shipments.
Strict compliance with varying government regulations, especially for international shipments, drives the need for wireless trackers throughout the transit process. Transmitting data on cold chain profiles of foods, vaccines or volatile materials requires higher levels of security to prevent contamination and tampering. Many Wi-Fi HaLow SoCs available today include secure boot technology that enables trusted over-the-air (OTA) platform connections of encrypted data. Wi-Fi HaLow data bandwidth enables larger amounts of stored data to be transferred than possible using simple RFID tags or other proprietary wireless network solutions.
Robust Signal Strength for Pickers and Scanners
In addition to providing the bandwidth for secure data transmission, wireless IoT networks for factory automation, logistics and asset management must establish robust connections. For example, mobile workers and automated robotic product handlers on manufacturing and warehouse floors require the flexibility of traversing large expanses without losing connectivity. Wi-Fi HaLow supports robust connections over long distances, enabling forklift operators to move freely across multiple aisles and robotic equipment to deliver stored goods to distant sorting lines.
In warehouses and other large-scale storage environments, signal strength is not the only challenge facing wireless networks. The availability of power is also a concern. Many popular handheld IR scanners, printers, and picking assistance devices must be recharged on a daily basis or plugged into wall power sources to maintain uninterrupted wireless connections. The power required for a Wi-Fi HaLow communications link is a small fraction of the power drain from proprietary wireless solutions. This energy efficiency greatly extends battery life and the time mobile devices can move around the warehouse floor instead of remaining plugged into wall sockets. Wi-Fi HaLow can also be used as a long-distance bridge for RFID scanners requiring mobility to different areas of the warehouse or loading dock.
Bandwidth for Large, High-Density Factories and Warehouses
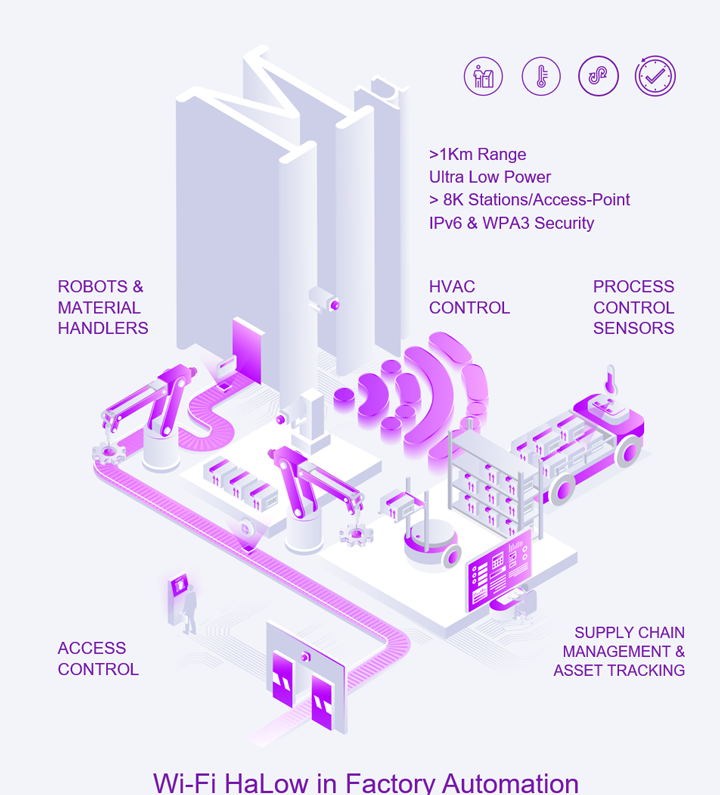
Today’s large, dense factory and warehouse environments require advanced network infrastructure capable of providing ample bandwidth and enough capacity to support a multitude of wireless sensors and on-site mobile devices. IT organizations for factories, shipping companies and warehouse facilities must support personnel, equipment, robots, security devices, inventory tracking systems, and building automation systems for HVAC, power, lighting and safety.
Legacy wired networks for factory automation are based on proprietary protocols with an infrastructure that is aging quickly and can no longer serve the emerging needs of modern equipment in terms of reach, capacity and security. Supplying wireless service coverage for a 100,000-square-foot factory or warehouse using conventional Wi-Fi in the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz bands requires many dozens of access points. Each AP will need a Power-over-Ethernet (PoE) cable connection back to a wiring closet switch. In addition, a server-based controller may be required to manage security and roaming. The maximum density of clients served in this manner with conventional Wi-Fi is quite low, ranging in the hundreds of clients per AP.
In contrast, a Wi-Fi HaLow AP signal can reach 10x farther, covering 100x the area and 1000x the volume of conventional 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi. The penetration of sub-GHz signals through manufacturing floor and multiple shelves of inventory outperforms 2.4 GHz signals used by traditional Wi-Fi. Each HaLow AP can support up to 8,191 client devices, which is considerably more than possible with conventional Wi-Fi which maintains the network deployment simple and low cost as Wi-Fi HaLow requires the addition of only a few new APs or HaLow expansion radio cards. Wi-Fi HaLow connectivity also can be added to existing factories and warehouse infrastructure without impacting the wireless performance of high bandwidth networks or wiring closets.
Factory Safety and Security
Surveillance cameras and motion detectors combined with smart access technology are effective tools for monitoring production lines and goods in transit or storage. For example, the combination of connected door locks and smart lighting fixtures can address critical aspects of building safety and help protect raw materials, finished goods and even personnel involved in the manufacturing, warehousing, and shipping process. Wi-Fi HaLow provides ample bandwidth to support wireless cameras and sensors deployed in hard-to-reach places where wireline power cannot be supplied. Leveraging the long-range capabilities of Wi-Fi HaLow, signal coverage can be extended well beyond a warehouse using wireless tags and tracking devices. Shippers can thus track and locate lost pallets and high-value assets at any time.
Connecting the Future of Factory Automation and Supply Chain Logistics
As global manufacturing and supply chains grow increasingly complex and interconnected, companies around the world are leveraging the power of wireless IoT technology to streamline factory automation, logistics and asset tracking. Wi-Fi HaLow provides an optimal protocol for factory automation and end-to-end, real-time asset management. HaLow overcomes the distance limitations, network congestion and higher power consumption of conventional Wi-Fi and other proprietary protocols, as well as the limited number of wireless devices that can be connected to a single access point. These limitations impede new IoT-centric supply chain models that are emerging across industries. By addressing these challenges, Wi-Fi HaLow is gaining momentum in the logistics and asset management market as a standards-based wireless solution that delivers an optimal balance of long range, high capacity, low power, high data rates and low cost of deployment.
About Kevin Daly
Kevin Daly is Vice President of Sales for Morse Micro, a fast-growing wireless integrated circuit solutions company that is reinventing Wi-Fi for the Internet of Things (IoT).
The content & opinions in this article are the author’s and do not necessarily represent the views of ManufacturingTomorrow
Comments (0)
This post does not have any comments. Be the first to leave a comment below.
Featured Product


