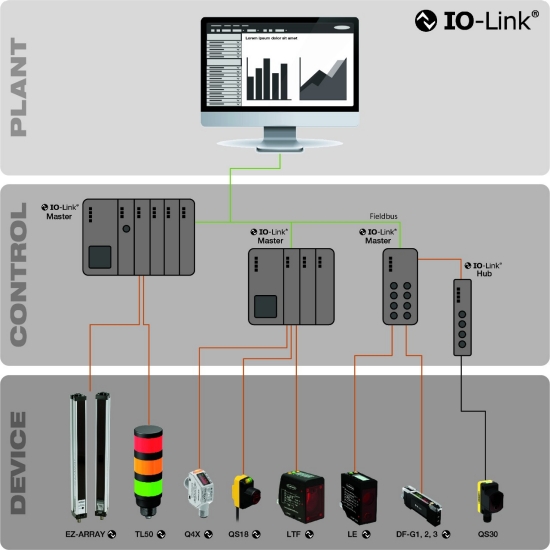
IO-Link (IEC61131-9) is an open standard serial communication protocol that allows for the bi-directional exchange of data from sensors and devices that support IO-Link and are connected to a master.
What is IO-Link
Contributed by | Banner Engineering
Reprinted with Permission from Banner Engineering – View original article here:
IO-Link has received increasing attention of late, but there are many misconceptions about what it is and its impact on industrial applications. This article explains what IO-Link is (and is not) and the advantages IO-Link offers to a wide variety of applications.

What is IO-Link?
 IO-Link (IEC61131-9) is an open standard serial communication protocol that allows for the bi-directional exchange of data from sensors and devices that support IO-Link and are connected to a master. The IO-Link master can transmit this data over various networks, fieldbuses, or backplane buses, making the data accessible for immediate action or long-term analysis via an industrial information system (PLC, HMI, etc.). Each IO-Link sensor has an IODD (IO Device Description) file that describes the device and its IO-Link capabilities.
IO-Link (IEC61131-9) is an open standard serial communication protocol that allows for the bi-directional exchange of data from sensors and devices that support IO-Link and are connected to a master. The IO-Link master can transmit this data over various networks, fieldbuses, or backplane buses, making the data accessible for immediate action or long-term analysis via an industrial information system (PLC, HMI, etc.). Each IO-Link sensor has an IODD (IO Device Description) file that describes the device and its IO-Link capabilities.
It should be noted that IO-Link is not another fieldbus—but rather a point-to-point communication protocol between a compatible IO system and a field device. Because IO-Link is an open standard, devices can be integrated in virtually any fieldbus or automation system.
5 Advantages of IO-Link
There are many advantages of an IO-Link system including standardized and reduced wiring, increased data availability, remote configuration and monitoring, simple device replacement, and advanced diagnostics.
Together these capabilities result in:
- Overall reduced costs
- Increased process efficiency
- Improved machine availability
The benefits of IO-Link are especially significant in applications in that experience frequent changeover and are severely impacted by extended and/or unplanned downtime.
Keep reading to learn more about how IO-Link can benefit your business.
Or for product information, see the full list of Banner products with IO-Link.
1. STANDARDIZED AND REDUCED WIRING
A critical benefit of IO-Link for many industries is that IO-Link does not require any special or complicated wiring. Rather, IO-Link devices can be connected using the same cost-effective standard unshielded 3-wire cables as conventional discrete I/O—which helps keep wiring simple. In addition, IO-Link also eliminates the need for analog sensors and reduces the variety of cord sets required for sensors, which saves inventory costs. IO-Link also supports a master-slave configuration with passive connection points, which further reduces wiring requirements.
2. INCREASED DATA AVAILABILITY
Data availability is a powerful advantage of IO-Link that has far-reaching implications. Access to sensor-level data helps ensure the smooth operation of system components, streamlines device replacement, and enables optimized machine maintenance schedules—all of which save costs and reduce the risk of machine downtime.
There are three primary data types made available via IO-Link communication, which are categorized as either cyclic data (data automatically transmitted on a regular basis) or acyclic data (data transmitted as needed or upon request).
- Process Data refers to the information that the device reads and transmits to the master—such as the distance reading on a laser measurement sensor. Process data can also refer to information that is transmitted to the device from the master (such as messages sent to a tower ligh indicating which color segments should be illuminated). Process data is transmitted cyclically in a defined data frame. In addition, value status data—indications of whether or not process data is valid—is transmitted along with process data.
- Service Data—also called Device Data—refers to information about the sensor itself such as parameter values, model and serial numbers, device descriptions, etc. Service data can be both written to the device or read fromthe device acyclically.
- Event Data refers to notifications such as error messages or maintenance warnings (e.g. device overheating, dirty lens) that are transmitted acyclically from the IO-Link device to the master whenever an event occurs.
This wealth of valuable data made available through IO-Link is integral for the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and Industry 4.0 initiatives.
3. REMOTE CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING
With IO-Link, users can read and change device parameters through the control system software, enabling fast configuration and commissioning that saves time and resources. In addition, IO-Link allows operators to dynamically change the sensor parameters from the control system as needed—such as in the case of product changeover—which reduces downtime and allows machines to accommodate greater product diversity. This is especially important in consumer packaged goods applications where the demand for variety in packaging is continually increasing.
In addition, the ability to monitor sensor outputs, receive real-time status alerts, and adjust settings from virtually anywhere allows users to identify and resolve problems that arise on the sensor level in a timely manner. This also means that users can make decisions based on real-time data from the machine components themselves, which can reduce costly downtime and improve overall efficiencies.
4. SIMPLE DEVICE REPLACEMENT
In addition to the ability to remotely adjust sensor settings, IO-Link’s data storage capability also allows for automated parameter reassignment in case of device replacement (this functionality is also known as Auto-Device Replacement or ADR). Users can import existing sensor parameter values into a replacement sensor for seamless replacement, getting the new device up and running as quickly as possible.
5. EXTENDED DIAGNOSTICS
IO-Link provides users with visibility into errors and health status from each device. This means that users can see not only what the sensor is doing but also how well it is performing—a valuable insight into a machine’s efficiency. In addition, extended diagnostics allow users to easily identify when a sensor is malfunctioning and diagnose the problem without shutting down the line or machine.
The combination of both real-time and historic data made available via an IO-Link system not only reduces troubleshooting efforts as issues arise but also allows for optimization of machine maintenance schedules, saving costs and increasing efficiency in the long term.
The content & opinions in this article are the author’s and do not necessarily represent the views of ManufacturingTomorrow
Comments (0)
This post does not have any comments. Be the first to leave a comment below.
Featured Product