Using the engineering software validated by the Pacific Northwest National Lab lead team, manufacturers will be able to "see" what the structural characteristics of proposed carbon fiber composites designs would be like before its molded.
PlastiComp Part of Team Working to Accelerate Development of Affordable Carbon Fiber Composites
Contributed by | PlastiComp
By model year 2025, U.S. regulations mandate that the average fuel economy standard meets 54.5 miles per gallon, a 60% improvement over the 35.5 MPG required of vehicles now. Reducing the weight of vehicles is one of many ways auto manufacturers are looking to improve the fuel efficiency of cars and trucks. Indeed, reducing the weight of a vehicle by 10% yields a 6 to 8% increase in fuel economy. One of the most promising lightweight material systems to replace heavy steel on automobiles is carbon fiber reinforced plastics.
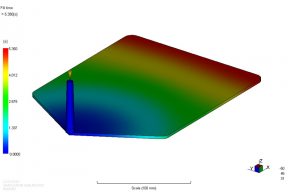
Mold filling predicted for 2D plaque using the Autodesk Moldflow software.
However, while stronger and lighter than steel, carbon fiber composites are relatively expensive, resulting in the need for judicious use of the material. For widespread adoption of carbon fiber to occur, new, economical composites that meet mechanical and safety requirements — such as long carbon fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resins like polypropylene and nylon — need to be developed. Carbon fiber properties, however, are more complicated to model than metal properties as carbon fiber composites depend on complex features such as the fiber loading as well as fiber length distribution and fiber orientation that occur in the material due to the manufacturing process.
The Quest to Lighten the Automotive Load
To accelerate the development of new, economical long carbon fiber composites, PNNL worked with a team of leading experts to develop a series of engineering tools. Team members included:
- An automotive manufacturer (Toyota)
- A tier one part producer (Magna)
- A long carbon fiber material and technology supplier (PlastiComp)
- A leading process modeling software provider (Autodesk)
- University research partners (University of Illinois, Purdue University, and Virginia Tech).
Funded by DOE’s Office of Vehicle Technologies Lightweight Materials Program, the team created software tools that successfully predict the fiber orientation and length distribution of complex carbon fiber thermoplastic parts.
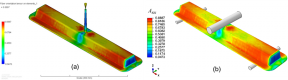
Fiber orientation prediction in 3D complex part using the Autodesk software (Left) that was imported into the 3D ABAQUS® model (Right) for stiffness performance prediction using the PNNL-developed Eshelby-Mori-Tanaka Approach to Non-Linear Analysis (EMTA-NLA) model in ABAQUS® (Right).
Current development processes of composite components require carmakers to build molds, mold parts, and test them. It’s a long, arduous process, slowing the advance of new, more cost-effective carbon fiber composites in automobiles. Using the engineering software validated by the PNNL-lead team, manufacturers will be able to “see” what the structural characteristics of proposed carbon fiber composites designs would be like before it’s molded. The tools allow manufactures and auto part designers to experiment and explore new ideas at a much faster rate.

Mold fill profiles of the 3D complex part.
To predict fiber orientation and fiber length distribution in molded components, the team leveraged Autodesk Moldflow software, based on models originally developed by Professor Charles Tucker and coworkers. With guidance from Toyota, PlastiComp, and Magna and materials from PlastiComp, long carbon fiber components were molded and the fibers extracted for measurement by Purdue University and Virginia Tech.
PNNL then compared the predicted properties from the simulation software to the test results of the molded fibers to validate the accuracy of the software and models. PNNL found the software tool successfully predicted fiber length distribution in all cases and fiber orientation in 88% of cases.
Additionally, as part of the project, PNNL worked with Magna and Toyota to analyze the performance gains and costs of long carbon fiber components versus standard steel and fiberglass composites. PNNL found the carbon fiber reinforced polymer composite technology studied could reduce the weight of automobile body systems by over 20%. However, production costs of carbon fiber components can be 10X higher than those of steel. The optimization of processes and structures using predictive tools could significantly reduce production costs, paving the way for greater use of carbon fiber in automobiles.
The content & opinions in this article are the author’s and do not necessarily represent the views of ManufacturingTomorrow
Featured Product

